China’s energy revolution is sparking a swifter global transition to clean power, according to a new study, meaning that, in two decades, the world could generate 40 percent of its power from renewable resources.
Fatih Birol, executive director of the International Energy Agency, a Paris-based energy policy advisory body, said the growth in China’s use of clean energy is reshaping forecasts of future energy usage.
“We see China becoming the leader by far in solar, wind, and electric cars, with less activity in coal and oil,” Birol said from the London launch of the IEA’s annual World Energy Outlook report. “China’s energy sector is changing, and, as such, it changes the global energy sector.”
Broad policy initiatives laid out by President Xi Jinping in 2014 and again this year as part of the country’s energy production and consumption strategy look to build a more secure, diverse, and efficient energy future for China.
“This strategy was reinforced weeks ago by President Xi at the 19th Communist Party of China National Congress,” Birol said. “It aims to put emphasis on environmental issues, and to ‘make the skies of China blue again’.”
China has become the world’s largest investor in renewable technology, and the country is increasing its solar and wind capacity at a record pace, driving down the cost of the technologies as it does so. The IEA predicts that, in 25 years, solar power will be the cheapest form of energy.
“There is a huge transformation in China’s economy, moving from an energy-intensive phase into a lighter, service-based economy,” said Laura Cozzi, head of the IEA’s Energy Demand Outlook Division. “The population is becoming wealthier, demanding cleaner skies, demanding more services.”
She said China is making investments in smart grids, wind and solar, “and soon, renewables will overtake coal in the energy mix”.
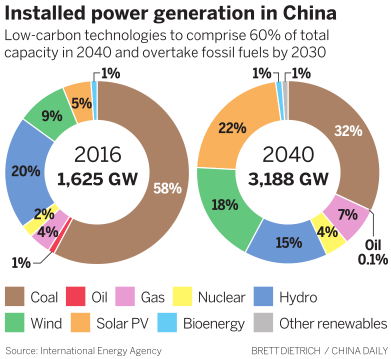
Cozzi said, if current energy policies remain in place, low-carbon technologies will comprise 60 percent of total capacity in China by 2040, and renewables are on course to overtake fossil fuels by 2030. Fossil fuels currently comprise 63 percent of installed capacity in China, with the vast majority-58 percent-coming from coal.
Rapid deployment of solar panels, led by China and India, will see solar power become the largest source of low-carbon energy by 2040, according to the IEA. By that year, renewables could account for 40 percent of total power generation around the world. Coal, which currently contributes 67 percent of generation, will fall to 40 percent.
The IEA predicts that, during the next two decades, the portion of China’s fossil fuel mix taken up by natural gas will almost double. The share of gas in China’s total installed capacity will rise from 4 percent to 7 percent by 2040, it says.
Natural gas produces less carbon dioxide and fewer pollutants than oil and coal when it burns and has emerged as the world’s fastest-growing fossil fuel, marking a geopolitical shift in traditional sources of energy. The shale oil and gas boom in the United States is proliferating as producers continue to unlock new resources in more cost-effective ways.
By the mid-2020s, the IEA predicts the US will become the world’s largest liquefied natural gas exporter and a net oil exporter by the end of that decade.
This is impacting oil and gas markets, challenging incumbent suppliers and provoking a reorientation of global trade flows. Consumers in Asia will account for more than 70 percent of global oil and gas imports by 2040, according to the IEA.